Mastering The Warehousing Management System To Achieve Peak Performance
In today’s fast-paced business environment, where customer demands and market dynamics are ever-evolving, the role of an efficient Warehouse Management System (WMS) cannot be overstated. As e-commerce and global supply chains become integral parts of businesses, the ability to adapt and optimize warehouse processes is a strategic necessity. A well-structured WMS not only ensures that operations run smoothly but also empowers businesses to respond swiftly to market changes, reduce costs, and elevate customer satisfaction.
Mastering the Warehousing Management Systems is the key to achieving peak performance in logistics. Whether you’re dealing with inventory, orders, or overall warehouse operations, a well-implemented WMS can enhance efficiency and accuracy, providing real-time insights crucial for a seamless supply chain. By delving into the intricacies of different WMS types, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their unique needs, fostering a logistics strategy that stands resilient in the face of industry challenges.
What does WMS stand for?
WMS stands for “Warehousing Management System”
This software system is designed to streamline and optimize the day-to-day operations within a warehouse or distribution center. It encompasses a range of tasks, including inventory management, order fulfillment, picking and packing, shipping, and overall warehouse optimization. WMS aims to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and visibility in warehouse operations, providing real-time data and insights to improve the seamless flow of goods through the supply chain.
The Main Goal of WMS
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) aims to help warehouse managers enhance efficiency and productivity by utilizing diverse functionalities. This facilitates them to fulfill customer’s demands and sustain a competitive advantage in the market. According to a survey conducted in 2020, 80% of respondents anticipate that digital supply chains will become the prevailing model within the next five years. This underscores the crucial role of implementing systems such as WMS in staying aligned with the evolving industry landscape. Choosing the right warehouse solution for your business can differentiate you from the rest.
Types of Warehouse Management System (WMS)
Integrated ERP System/Module
A large network of contacts facilitates the connection with trustworthy carriers providing high-quality services tailored to the customer’s transportation requirements. This includes considerations for the appropriate type of truck, delivery times, and pricing. Ensuring the deliveries from the precise point of pick-up in Mexico or the U.S. to the exact destination in the opposing country. Most often preferential rates for freight shipping services between the U.S. and Mexico are established with a specialized freight forwarder focused on the North American region.
The Warehouse Management System (WMS) integrated into Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions facilitates smooth data sharing and automation features tailored for large enterprises. This variant of WMS provides a distinct advantage through seamless system integration, enabling real-time data exchange and visibility between the WMS and other critical systems, including inventory, accounting, and finance. It also works well for big companies because it gives them one place to handle all inventory in the warehouse.
According to a study by SelectHub, 95% of businesses experienced improved process efficiency with an ERP system.
Cloud-Based System
These systems are installed in the cloud and provide accessibility, affording heightened adaptability to accommodate dynamic market conditions and streamline scalability as businesses expand. Regular updates in cloud-based warehouse management facilitate a faster route to innovation, relieving users of the responsibility for system maintenance and updates.
The Cloud-Based system gives you a flexible and scalable way to manage your warehouse. It also lets you see and control things in real time. This type of WMS helps businesses improve their warehouse processes, spend less money, and work more efficiently by making workflows smoother and automating tasks.
According to Gartner, public cloud infrastructure workloads are predicted to experience at least 60% fewer security incidents than traditional data centers.
Standalone System
The Standalone WMS focuses its software solutions on warehouse management operations for small and medium-sized businesses. This system offers a way to focus on managing a warehouse without needing to connect with plenty of other systems. It stands on its own and comes with special features like keeping track of inventory, managing orders, and handling labor costs. It’s a choice for organizations with tight budgets and limited resources because it’s cost-effective and easy to set up.
A report by Software Connect indicates that these businesses can expect to spend between $4,000 and $10,000 on a standalone WMS system, making it a budget-friendly option.
Supply Chain Module
The Supply Chain Module WMS works with businesses with complicated supply chain software. It plays nicely with other solutions like accounting and business intelligence. By doing this, it gives a full view of the business and logistics chain, making everything clear and organized from start to finish.
The Operation of WMS
Inventory Management
This software offers real-time visibility into an organization’s inventory across various locations, encompassing items in transit and those stored. This software utilizes automatic identification and data capture (AIDC) technologies like barcodes or RFID for efficient tracking. Accurate inventory tracking and related practices are pivotal in ensuring orders are complete, delivered on time, and undamaged.
Fulfillment
Certain warehouses simplify order fulfillment through various techniques, including single-order picking, batch picking, zone picking, cross-docking, and additional strategies. All of these contribute to the optimization and efficiency of the order fulfillment process.
Delivery/Shipping
Warehouse systems are integrated into the transportation and logistics industry, where WMS offers diverse methods to accelerate the fulfillment process, including automated generation of bills of lading, packing lists, and invoices for shipments, along with the automatic dispatch of shipment notifications. Including real-time tracking features, companies can monitor the timely and accurate delivery of packages to their destinations. Top-tier warehouse operations consistently ensure that the majority of shipments leave the facility promptly and reach their destinations on schedule because it is crucial to the supply chains.
Metrics and Analytics Performance
The Warehouse Management System (WMS) is an automated process that gathers real-time data, replacing the need for manual data collection with speed and accuracy while minimizing key errors. The system monitors essential metrics such as on-time shipping, inventory, distribution, cost, and orders, to document this the system generates visual reports.
Optimal Space Utilization
It maximizes storage capacity improving the overall layout of the warehouse. The system evaluates floor space to create an optimal utilization of the space.
Cross-Docking Operations
Cross-docking in the Warehouse Management System (WMS) helps in functions such as the movement of goods from the receiving area to shipping, minimizing the requirement for storage. Through precise and timely information exchange and communication between the warehouse management system and the transportation system, the WMS facilitates a more efficient supply chain, accelerates order fulfillment, and lowers overall costs. This system has proven beneficial in industries such as transportation, freight forwarding, manufacturing, and more.
Safety Features
These features foster a secure work environment and safeguard against theft and damage. In terms of security, the WMS utilizes access control, surveillance cameras, alarm systems, inventory tracking, and environmental controls to mitigate the risks of theft and damage. There are key safety features integrated into warehouse management systems these functionalities are instrumental in guaranteeing the well-being and security of both the warehouse and its operations.
Key safety features:
- Hazard identification and risk assessment
- Forklift safety measures
- Material storage safety protocols
- Hazardous chemical management
- Fire detection and suppression systems
- Security measures
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Types of WMS
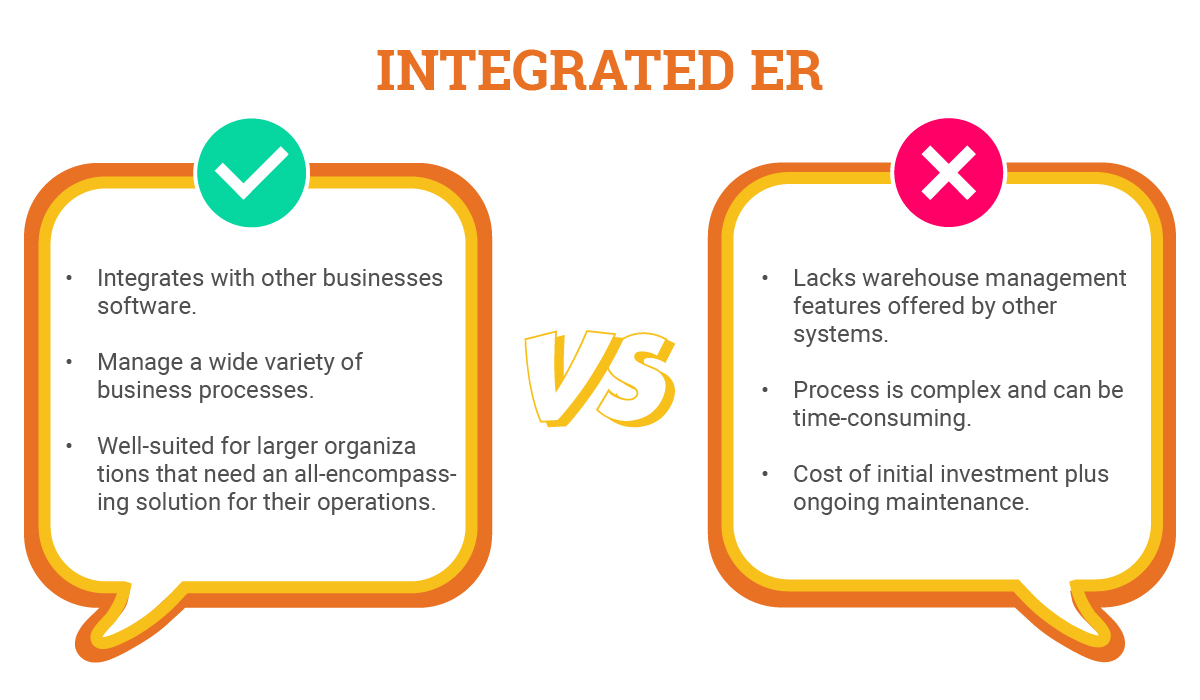
Integrated ER
Advantages
- The ERP Module WMS smoothly integrates with other businesses software, making data sharing easy and operations more efficient.
- It can manage a wide variety of business processes, not just limited to warehouse operations. This flexibility is beneficial for larger organizations seeking a comprehensive solution for their operations.
- Well-suited for larger organizations that need an all-encompassing solution for their operations.
- While feature-rich, it might lack specific warehouse features due to its broad focus. This could be a drawback for organizations with highly specialized warehouse management needs, particularly if they require advanced functionality for complex operations.
Disadvantages
- The ERP Module WMS lacks certain warehouse management features offered by other systems due to its broad focus.
- The implementation process is complex and can be time-consuming, complicated, and demands a substantial investment of resources.
- The overall cost can be significant, encompassing initial investment and ongoing maintenance. This may not be justified for businesses with simpler warehouse operations, because of the extensive focus and costs associated. The ERP Module WMS is less suitable for smaller businesses with more straightforward warehouse operations.
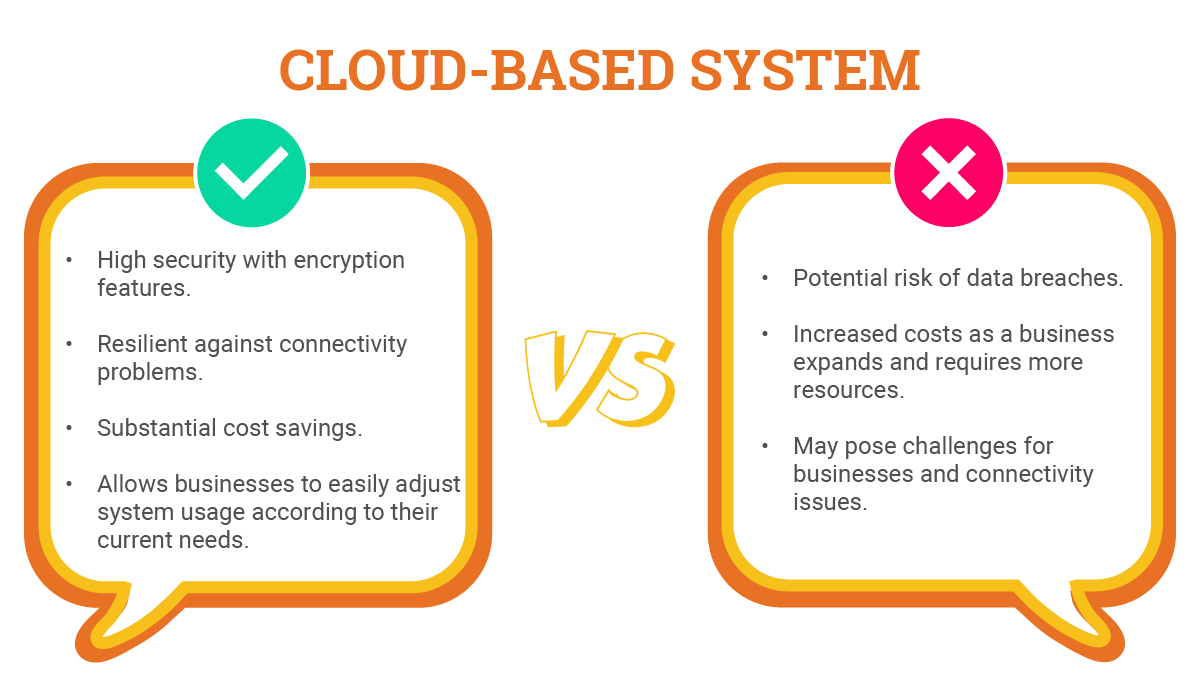
Cloud-Based System
Advantages
- Heightened security with features such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
- These modern systems are resilient against connectivity problems. They maintain functionality even during internet outages, thanks to features like local caching and data synchronization upon connection restoration.
- Cloud-based WMS can result in substantial cost savings. A study by Computer Economics found that 46% of businesses reported saving costs after transitioning to the cloud.
- Offers scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to easily adjust system usage according to their current needs. This ensures they only pay for the services they use, leading to additional cost savings. 31% of businesses cited scalability as the primary reason for adopting cloud services, according to a report by Statista.
Disadvantages
- Despite high-security standards, there is a potential risk of data breaches, as sensitive information is stored online, similar to any system with online data storage.
- While scalability is a significant advantage, it can also result in increased costs as a business expands and requires more resources.
- Integrating a cloud-based WMS with existing on-premise systems may pose challenges for businesses.
- Businesses experiencing unreliable internet connectivity may encounter difficulties accessing the system.
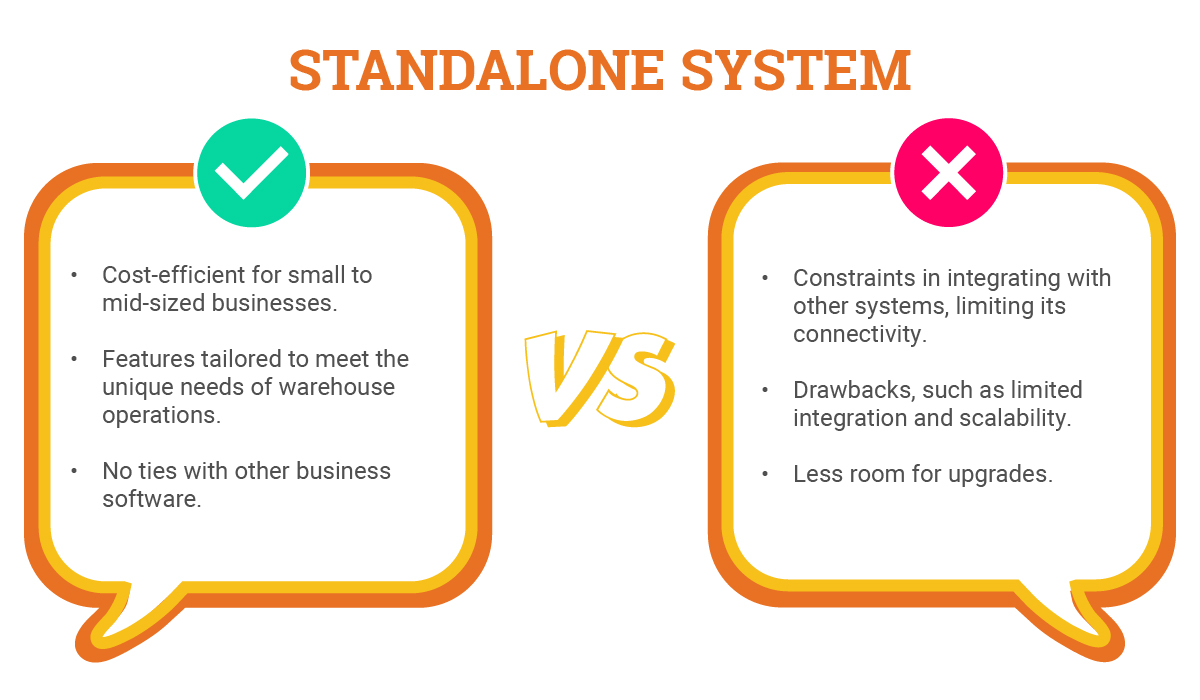
Standalone System
Advantages
- Standalone WMS systems are cost-efficient, especially for small to mid-sized businesses.
- These systems offer specialized features tailored to warehouse management, which are designed to meet the unique needs of warehouse operations.
- No ties with other business software, which makes them easy to implement. Fewer complexities involved in their setup and maintenance allow organizations to have their WMS up and running in a shorter time frame compared to integrated systems.
Disadvantages
- Standalone WMS has constraints in integrating with other systems, limiting its connectivity.
- Potential drawbacks, such as limited integration and scalability, should be carefully weighed when deciding on a warehouse management system.
- Provides specialized features tailored to warehouse management, catering to specific operational needs, and leaves less room for upgrades.
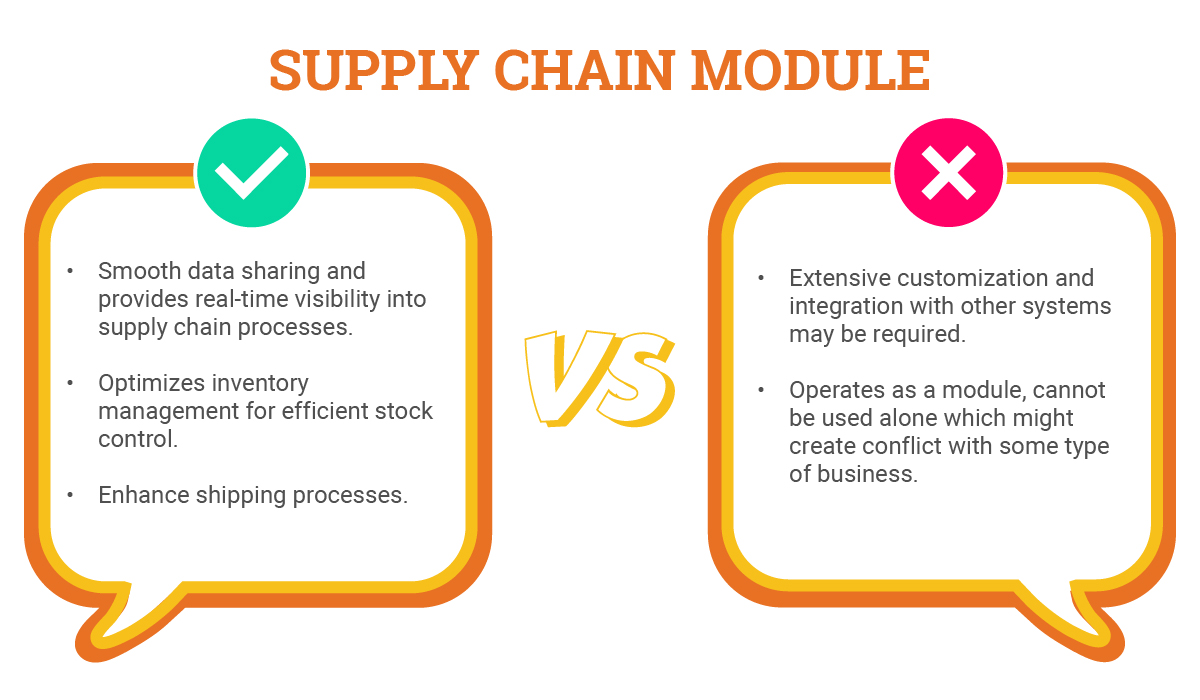
Supply Chain Module
Advantages
- Facilitates smooth data sharing and provides real-time visibility into warehouse operations and broader supply chain processes.
- Allows businesses to optimize their inventory management for more efficient stock control.
- Businesses can enhance shipping processes ensuring timely and accurate deliveries.
Disadvantages
- Because of its complexity, extensive customization and integration with other systems may be required, leading to higher costs and a steeper learning curve for users.
- It operates as a module that requires integration with other systems and cannot be used alone which might create conflict with some type of business.
Which software is the most popular in the transportation industry?
Cloud-based WMS becoming the usual thing in the industry.
It seems like more and more businesses are going for a cloud-based Warehouse Management System. The market is expected to grow a lot in the next 5-10 years, with a projected growth rate of about 16%. Small and medium-sized businesses especially like it because it’s flexible, scalable, and cost-effective.
Keeping up with the warehousing trends will make your business successful.
What type of Warehouse Management System do we use at Mexicom Logistics?
At Mexicom’s USA warehouse facility, located in Laredo, Texas. We rely on the Cloud-Based Warehouse Management System (WMS) to boost the effectiveness of our warehousing solutions. This cutting-edge system is crucial for optimizing various aspects of our operations, ensuring precision, real-time tracking, and smooth coordination. Whether it’s managing inventory or fulfilling orders, our WMS significantly contributes to the overall efficiency of our facility. This allows us to deliver top-quality warehousing solutions that cater to the diverse needs of our clients.
Our cloud-based WMS incorporates pictures for all transloading activities. We provide receipts and shipment notices to customers along with visual documentation. Managing inventory is a breeze, from pallet to SKU level, thanks to our fully automated system. Additionally, we offer an advanced reporting system tailored to meet client requirements. Our WMS seamlessly connects to the Transportation Management System (TMS) of the group, ensuring a comprehensive and integrated approach to our logistics operations.
In today’s dynamic business landscape, staying on top of warehousing trends is crucial for success. Cloud-based WMS, with its flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, is becoming the industry norm. As businesses evolve, choosing the right WMS, whether integrated, standalone, or supply chain-focused, plays a pivotal role in optimizing operations. Adopting these systems not only ensures efficiency and security but also keeps your business competitive in an ever-changing market.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of technological advancements promises even more innovations in warehousing management. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics are poised to revolutionize WMS capabilities, providing deeper insights and predictive analytics to further streamline operations. As businesses prepare for the future, they must stay tuned to emerging technologies. By investing in the right WMS technologies today, businesses can future-proof their operations and ensure sustained success in an ever-evolving market.







